Imaging Pipeline
Reconstruction
Registration
Detection
Segmentation
Reporting
XDMD develops AI for medical imaging covering every task in the pipeline.
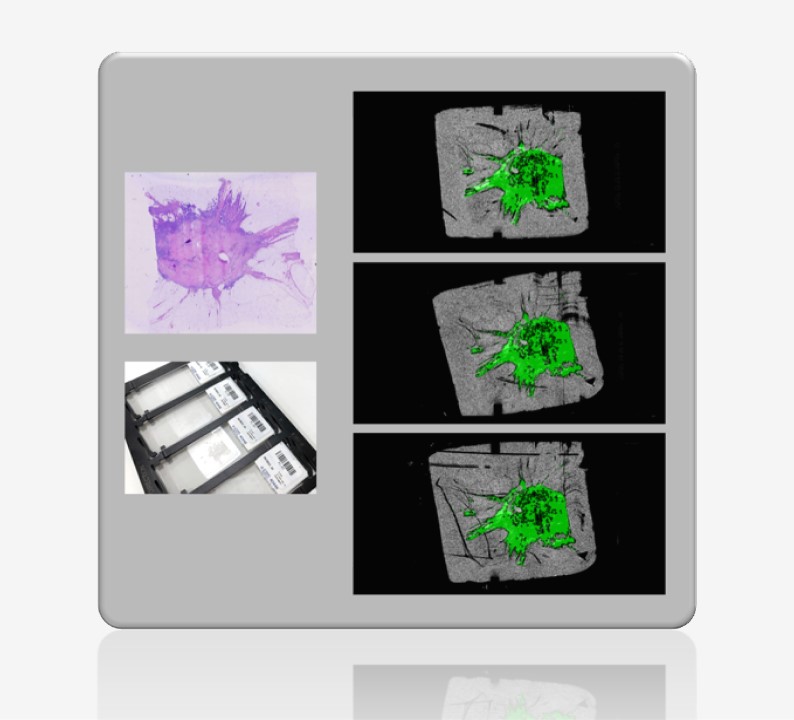
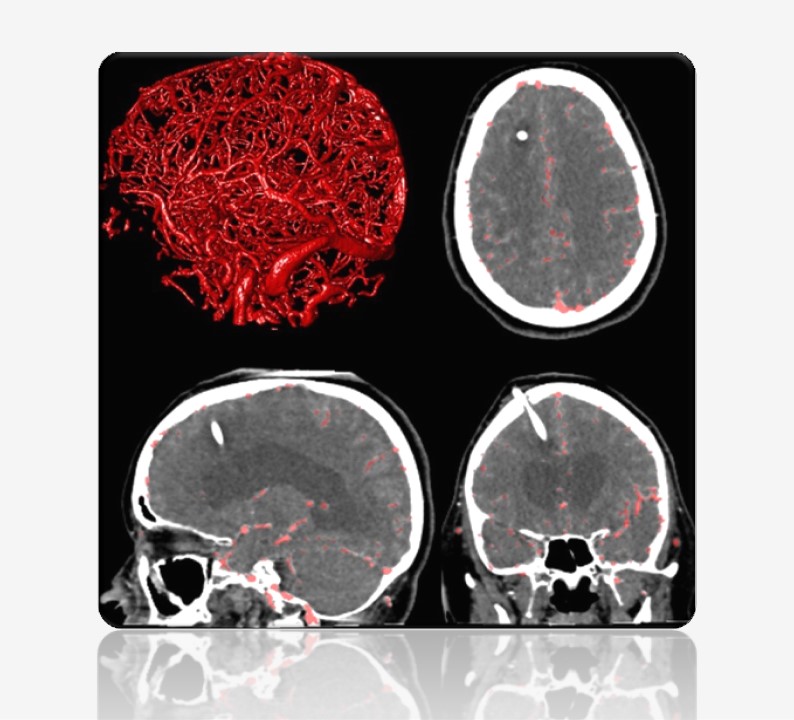
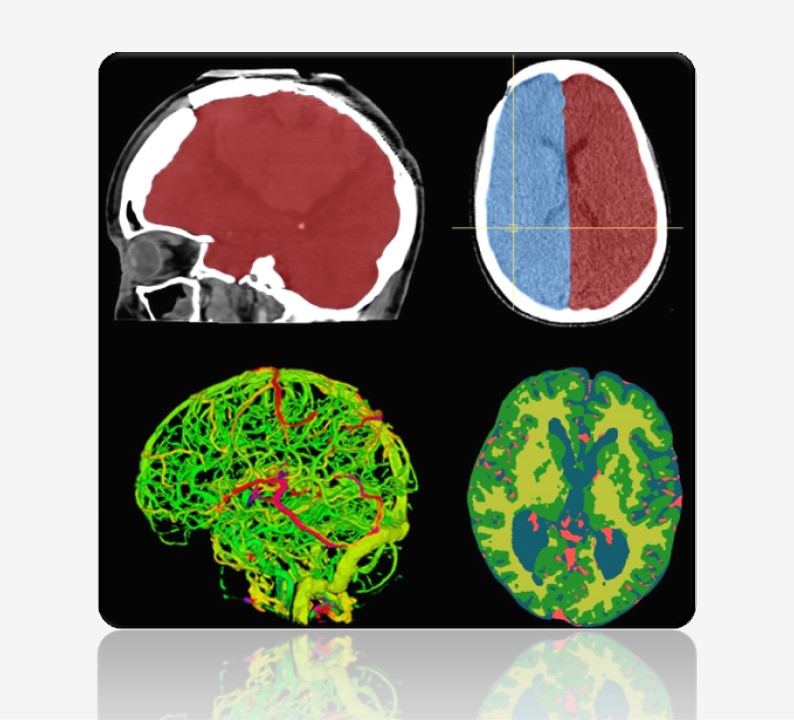
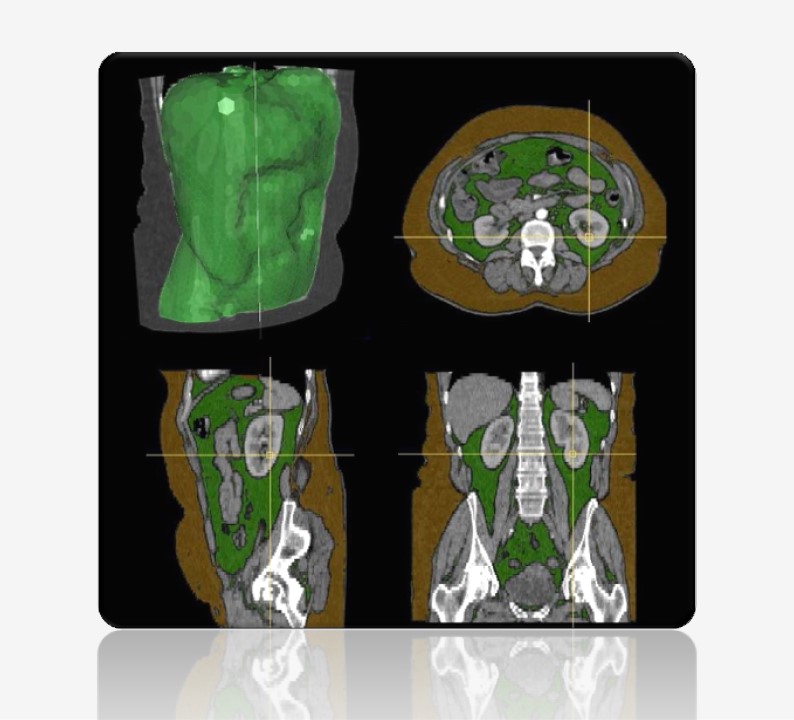
A typical imaging pipeline includes reconstruction, registration, detection, segmentation, and reporting. Image reconstruction transforms raw data from physical measurements into human-interpretable images. Registration is the spatial alignment of images. Segmentation is the contouring of objects or labeling of pixels in the image.
Among them, detection and segmentation are arguably the most important, as they involve interpretation and are often the primary reason for the scan. They form the core of nearly all workflows and products. Segmentation, for example, enables: quantification, visualization, characterization of anatomy, characterization of pathology, surgical planning and navigation, surgical scene understanding, treatment response monitoring, hemodynamic simulation, morpho-dynamic simulation, etcetera.
Solution Transfer
Image Analysis as Software
Tailored AI solutions for organizations needing to integrate image analysis into their own systems
Image Analysis as Function
Tailored AI solutions delivered via our cloud-based platform for functional and scalable image analysis
Basically, we provide the firmware for your medical device. The training algorithms enable continued development on-site. All software products have test routines, comprehensive documentation, and direct support. In addition, we can ensure compliance with applicable regulatory standards. The advantages of this approach are its direct integration and meeting the system constraints (e.g. available GPUs) which is desirable for medical devices that should operate fully independently.
As with our first solution, algorithms are tailored to your application, complete with test routines and comprehensive documentation. Images can be uploaded manually, or a secure connection can be established between our platform and your system for automated processing. We handle updates and ensure uptime. The advantages of this approach are that no in-house technical expertise is required and that computational resources can easily be scaled.
Our Approach
1. Problem and Context
To thoroughly understand the client’s needs, the specific image problem, and the overall context
First and foremost, we look at your images. We ask to share examples, allowing us to test some basic algorithms. Other activities include identifying key stakeholders and users, assessing functional requirements such as speed, accuracy, and robustness, determining relevant evaluation criteria, evaluating development needs including data, reference standards, and computational resources, and considering environmental factors such as available data, computational resources, human resources, and other constraints.
2. Legal and Regulatory
To ensure that software and data handling comply with all relevant legal and regulatory requirements
Compliance requirements vary based on the software’s intended use. For example, software developed to quantify a new imaging biomarker in research setting has different regulatory considerations than software intended for use in medical devices. Activities include identifying applicable regulations such as GDPR for data privacy and CE marking for medical devices, developing strategies to meet regulatory standards, and collaborating with legal experts to prepare necessary compliance documentation.
3. Planning and Risk Management
To organize the project effectively, ensuring timelines, resources, and risks are managed efficiently
Activities include defining key milestones and deliverables, assigning roles and responsibilities, systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, and establishing regular updates and feedback with the client. Risk management involves addressing potential regulatory and compliance challenges, data privacy and security issues, AI model performance limitations such as bias or drift, project scope changes, and resource allocation concerns.
4. Modelling and Engineering
To develop the core AI and machine learning models that will analyze your medical images
Activities include collecting and curating data, developing dedicated annotation tools (if required) and annotating data, collaborating with clinical specialists (primarily radiologists and pathologists) to accurately interpret and annotate images, building and training image processing algorithms and neural networks, rigorously testing to ensure model reliability and performance, and maintaining detailed records of models, algorithms, and workflows.
5. Integration or Connection
To seamlessly integrate the developed software with the client’s existing system or to host it as cloud-based platform and to establish a secure connection
Activities include ensuring compatibility with the client’s existing systems and software environment, developing a deployment plan, transferring the training environment to support continued model training on-site (if desired by the client), ensuring the solution scales seamlessly as needed for platform solutions, and providing training and user documentation.
6. Monitoring and Support
To assess the software post-deployment, ensure ongoing compliance, and provide continuous support
Activities include measuring key evaluation metrics established in the first stage, such as accuracy, speed, user satisfaction, and other outcome and process metrics, implementing systems to track software performance and compliance while monitoring for AI model drift and data quality issues, using feedback and monitoring data to enhance the software, and offering ongoing technical support, updates, and training.